- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |

- Speect »
- Documentation »
- Topic Guides »
The system architecture can be divided into two distinct parts, namely the engine and plug-ins.
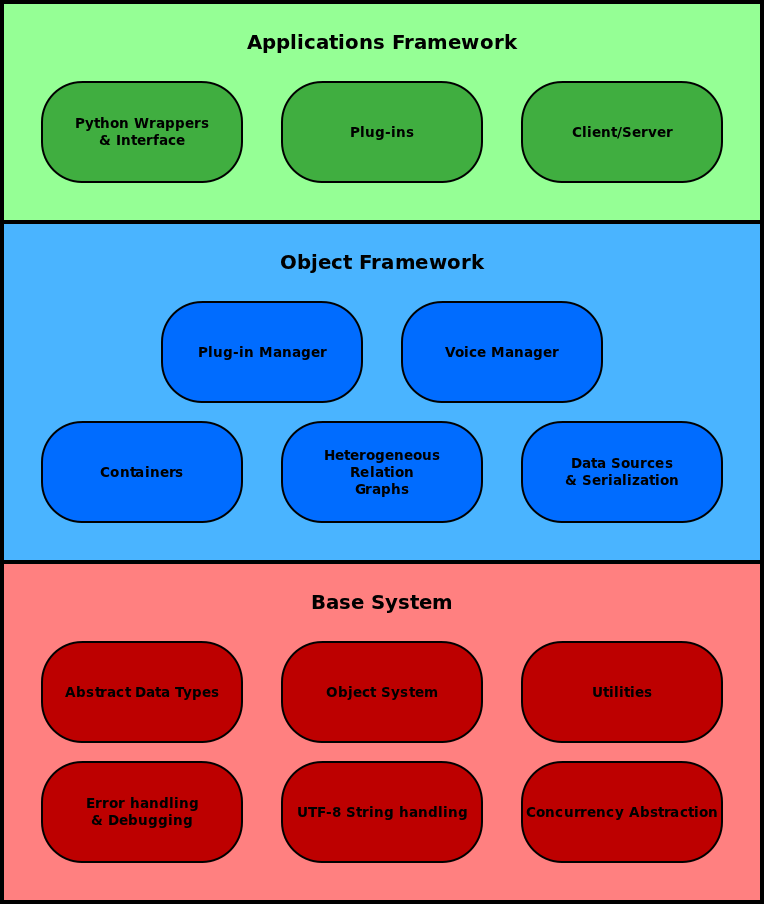
Figure 3: Speect Engine architecture.
Engine
The engine is completely independent of any language or waveform generation modules, and is solely responsible for the loading of voices and their associated data and plug-ins, and controlling the synthesis process. The engine is not dependent on any external libraries, and provides lower level functionality to the plug-ins. The engine consists of the base system and the object framework (see figure 3). The base system provides a low level library to the following modules:
- abstract data types (lists, buffers, hash tables),
- utilities (memory allocation, byte-swapping, timing, fundamental types, versioning, math and system path functions),
- error handling, debugging and logging,
- platform independent concurrency abstraction,
- UTF-8 string handling (character and string level functions, printing functions and regular expressions),
- and an object system.
The object system allows an object-oriented programming approach to the higher level libraries implemented in the object framework. These higher level libraries provide the following modules:
- containers (map, list),
- data sources and data serialization,
- heterogeneous relation graphs (HRGs) (for internal utterance representation),
- plug-in manager,
- and a voice manager.
Plug-ins
The plug-ins provide:
- new object types,
- interfaces to voice data (linguistic and acoustic),
- modules to do processing on utterance structure (utterance and feature processors), and
- the scripting language interface.